In a world facing numerous issues that stem from climate change, it is important to adapt our current processes, lifestyles, and activities that could further damage our environment. Human activities heavily influence climate change, but everyone can take steps to reduce their actions’ negative impact on the environment. One huge breakthrough in the scientific world is artificial photosynthesis. Although in its early stages, artificial photosynthesis uses a plant’s existing system to develop fuels such as ethylene, methane, or other fuels. Hopefully, in the future, it will reduce the need for fossil fuels and provide more sustainable fuel options.
Nanoparticle materials of different shapes and particle sizes are used as catalysts to mimic key photosynthesis functions. These functions include absorbing sunlight and transferring the electrons required to start chemical reactions in energy production. There are several challenges and benefits to nanoparticle materials in artificial photosynthesis, which will be discussed throughout this blog post.
How Nanoparticle Materials are Used for Artificial Photosynthesis
Nanoparticle materials are used in artificial photosynthesis to convert light or water into clean hydrogen fuel, considered a sustainable energy source. This process has significant advantages to the future of generating, storing, and transporting energy as it offers a substitute for fossil fuels in photosynthesis and produces a fuel that can be used for a wide range of applications. Artificial photosynthesis is conducted within electrolyser cells by using solar cells to absorb sunlight for energy and a catalyst to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. During this process, carbon dioxide hydrogenates to produce ethylene and other fuels.
Challenges of Artificial Photosynthesis
There are some challenges with using nanoparticle materials with artificial photosynthesis. However, this is no surprise, as artificially replicating any natural process can be difficult, if not impossible, in some cases. The difficulties with artificial photosynthesis include finding the most efficient catalysts and light-harvesting systems. There are also challenges in increasing the efficiency of conversion to high-order hydrocarbons and reducing the production of carbon monoxide.
Applications of Nanoparticle Materials for Artificial Photosynthesis
We’ve already mentioned that carbon dioxide can be converted into ethylene and other valuable fuels, which can be conducted through electrochemical conversion technology. Ethylene production is significant, and ethylene itself is often referred to as the ‘rice of the industry’ because it can be used to produce a range of polymers, plastics, and chemical products. As more research has been carried out, it was identified that more high-performance catalysts were required for artificial photosynthesis. These have since been developed and can be used to produce a broader range of valuable chemicals.
Nanotechnology can develop nanoparticle materials through a bottom-up or top-down approach to engineer materials with unique properties suitable for artificial photosynthesis. Nanoparticles are used as catalysts and can support generating high-energy hydrocarbons and breaking down carbon dioxide to produce fuels such as ethylene.
Breakthrough Research on Catalysts
To continue the topic of using nanoparticle materials as catalysts, Dr. Yun-Jeong Hwang and her team at the Clean Energy Research Center of the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST) have researched and discovered the benefits of using a copper-based catalyst during ethylene production from electrochemical CO2 reduction. This includes copper and copper oxides.
How Can Nikalyte Help?
Nikalyte has more than 20 years of experience developing outstanding nanoparticle deposition equipment for various applications. Our equipment is suitable for novice and experienced users alike and offers complete user control over the size and composition of nanoparticles.
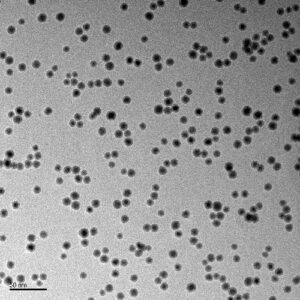
We mentioned research shows that copper-based catalysts have shown to be effective during artificial photosynthesis, and Nikalyte can help with this. Our technology can generate copper and copper oxide with high surface area to volume. We utilise a room temperature process that enables copper nanoparticle (Cu NP) coating of sensitive and thin substrates without causing damage. Nikalyte’s NL50 and NL-UHV instruments can be used for these processes to support artificial photosynthesis, as well as a wide range of other scientific applications.
Contact a member of Nikalyte today to learn more about how nanoparticle materials are used in artificial photosynthesis and how our products can support the process.

