A practical guide to magnetron-based thin film deposition
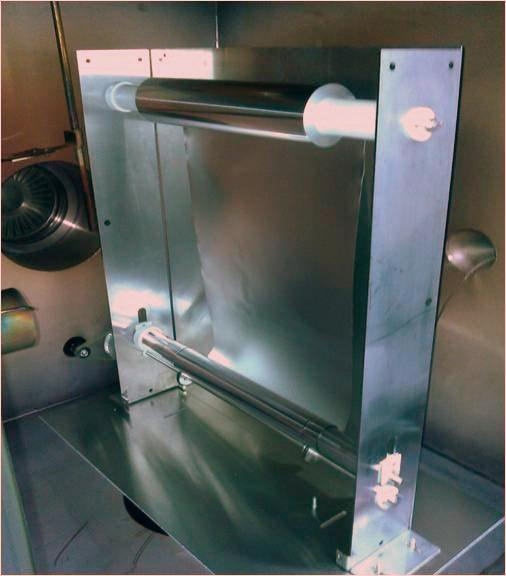
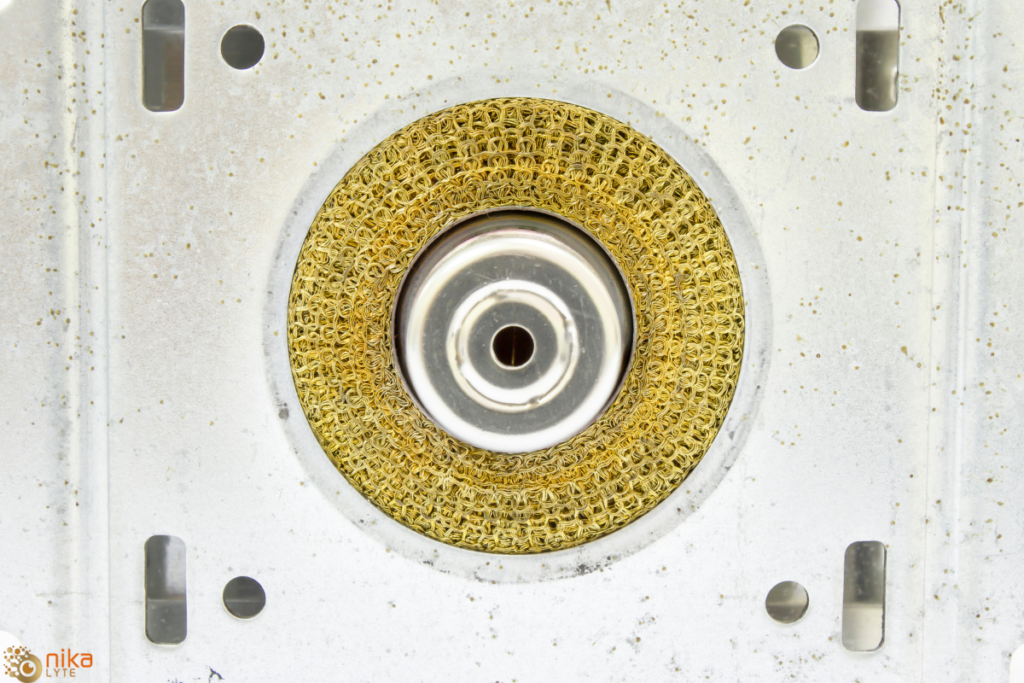
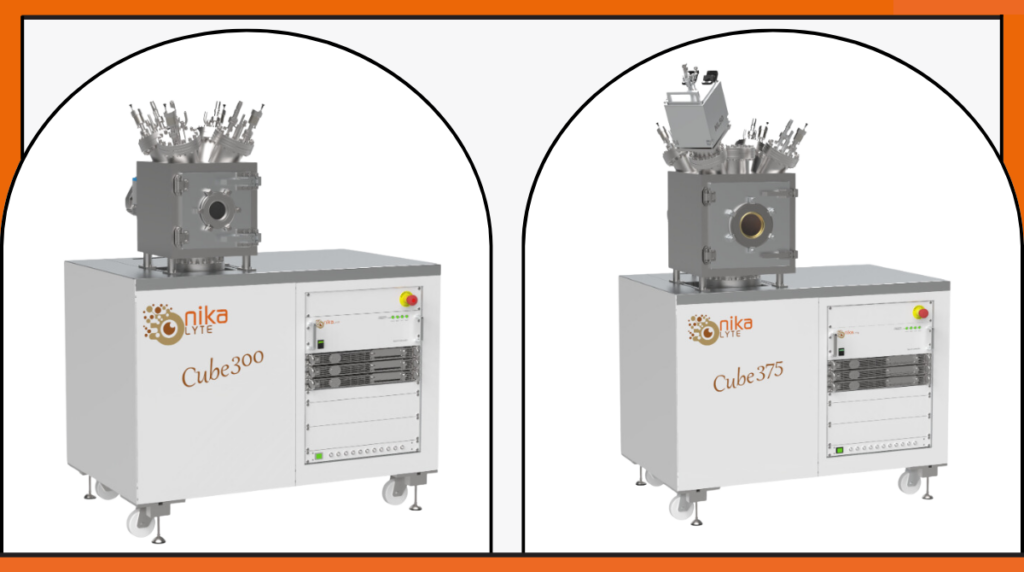
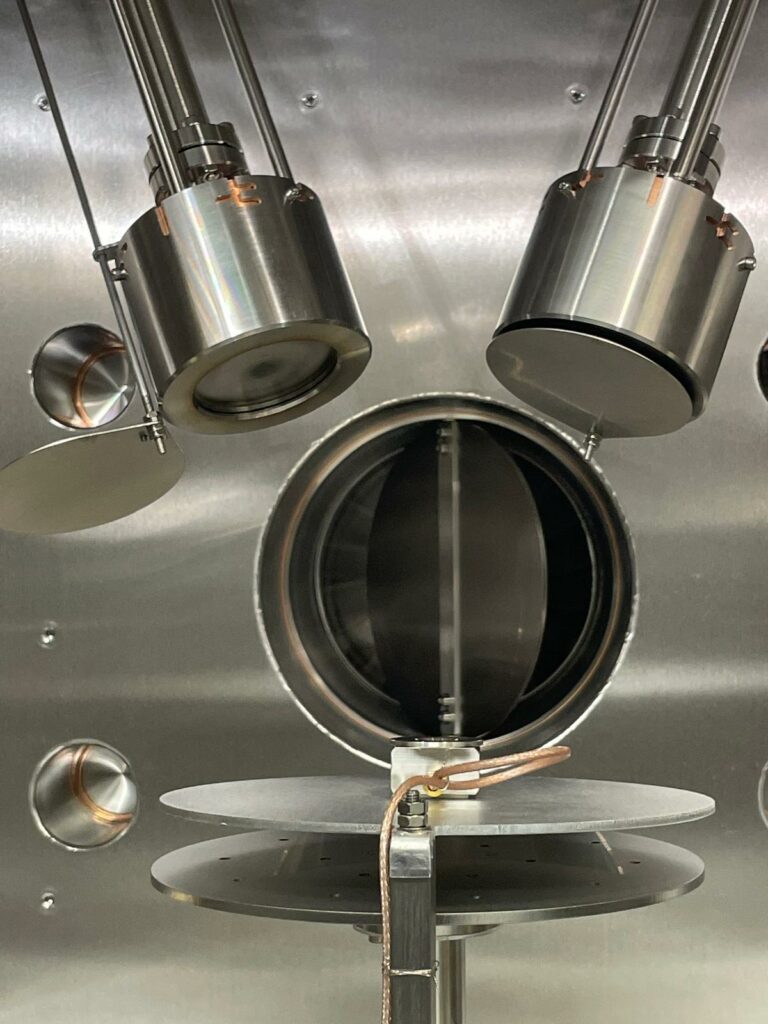
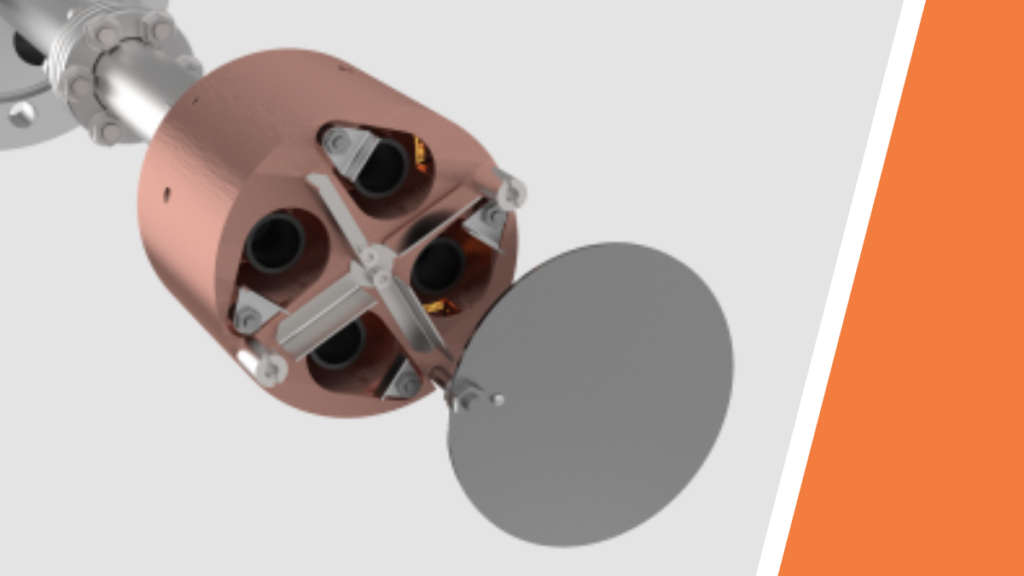
Thin films are at the heart of modern technology, used in everything from semiconductor devices to optical coatings and protective layers. Magnetron-based thin film deposition is one of the most effective methods for producing high-quality coatings with exceptional uniformity, adhesion, and material control. By utilizing plasma to transfer material from a target onto a substrate, […]
A practical guide to magnetron-based thin film deposition Read More »